Collections
Table of Contents
What is it?
Java Collections framework: available, efficient, bug-free implementations of many key data structures
Most classes are in java.util.*
Collections framework
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/collections/overview.html
- A collection is an object that represents a group of objects (such as the classic Vector class).
- A collections framework is a unified architecture (interface and classes) for representing and manipulating collections (group of objects), enabling collections to be manipulated independently of implementation details.
- Java collections framework provides a standard programming interface to many of the most common abstractions, without burdening the programmer with too many procedures and interfaces.
Primary advantages
The primary advantages of a collections framework are that it:
- Reduces programming effort by providing data structures and algorithms so you don’t have to write them yourself.
- Increases performance by providing high-performance implementations of data structures and algorithms. Because the various implementations of each interface are interchangeable, programs can be tuned by switching implementations.
- Provides interoperability between unrelated APIs by establishing a common language to pass collections back and forth.
- Reduces the effort required to learn APIs by requiring you to learn multiple ad hoc collection APIs.
- Reduces the effort required to design and implement APIs by not requiring you to produce ad hoc collections APIs.
- Fosters software reuse by providing a standard interface for collections and algorithms with which to manipulate them.
What does the collections framework consists of?
The collections framework consists of:
- Collection interfaces. Represent different types of collections, such as sets, lists, and maps. These interfaces form the basis of the framework.
- General-purpose implementations. Primary implementations of the collection interfaces.
- Legacy implementations. The collection classes from earlier releases, Vector and Hashtable, were retrofitted to implement the collection interfaces.
- Special-purpose implementations. Implementations designed for use in special situations. These implementations display nonstandard performance characteristics, usage restrictions, or behavior.
- Concurrent implementations. Implementations designed for highly concurrent use.
- Wrapper implementations. Add functionality, such as synchronization, to other implementations.
- Convenience implementations. High-performance “mini-implementations” of the collection interfaces.
- Abstract implementations. Partial implementations of the collection interfaces to facilitate custom implementations.
- Algorithms. Static methods that perform useful functions on collections, such as sorting a list.
- Infrastructure. Interfaces that provide essential support for the collection interfaces.
- Array Utilities. Utility functions for arrays of primitive types and reference objects. Not, strictly speaking, a part of the collections framework, this feature was added to the Java platform at the same time as the collections framework and relies on some of the same infrastructure.
Collection Interfaces
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Collection.html
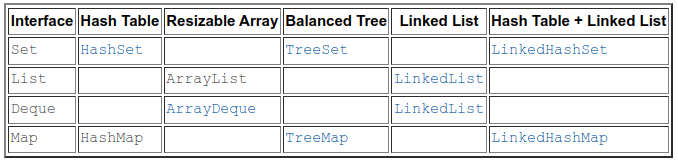
Collection implementations
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/collections/overview.html
Tags
- Collections - Arrays
- Collections - Iterators and Enumeration
- Collections - Java List interface
- Collections - Vector
- Collections - Vectors vs Arrays
- Collections - ArrayList
- Collections - Linked lists
- Collections - Linked List vs Arrays and ArrayLists
- Collections - Arraylist vs Arrays
- Collections - ArrayList vs Vector
- Collections - Comparing two lists
- Collections - Sorting ArrayList of user-defined objects
- Collections - Map interface
- Collections - Set interface
- Collections - Synchronized collections
- Java Streams Api
- Avoid if-else statements using collections
- Collections - Iterable collections and Iterators
- Collections - Reconcile objects in two collections
- Collections - Infinite Lists
- Collections - Helpful utility libraries
- ConcurrentModificationException
- Java object equality