Spring Cloud Stream
What is a stream?
- Continuous flow of data
- Incrementally processed
What is Spring Cloud Stream?
A framework (a Spring module) for building message-driven (event-driven) Spring Boot microservices for real-time stream processing.
You can learn more about the framework from the project-site, documentation, and samples.
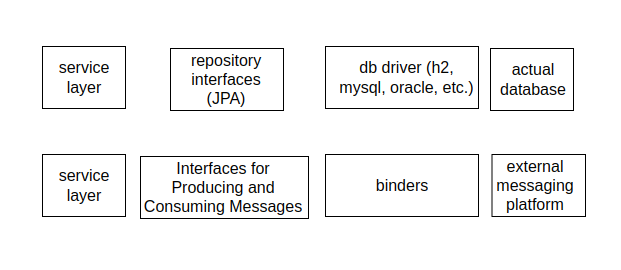
Spring Cloud Stream - Analogy with non-cloud patterns
For an analogy between traditional Spring Data JPA (does not use spring cloud stream) and Spring Data R2DBC (uses spring cloud stream)
Spring Cloud Stream - Programming Model
https://dataflow.spring.io/docs/stream-developer-guides/programming-models/
Binders, Bindings and Binding names
Spring Cloud Stream - Binders, Bindings and Binding names
Interfaces for Producing and Consuming Messages
Spring Cloud Stream - interfaces for Producing and Consuming Messages
Scaling up
To scale up our Spring Cloud Stream applications we need to launch additional instances of each microservice. When we do that, a single order is received by all the running instances of every microservice. This is exactly how topic exchanges work – the message sent to the topic is received by all consumers, which are listening on that topic. Fortunately, Spring Cloud Stream is able to solve that problem by providing a solution called consumer group. It is responsible for guaranteeing that only one of the instances will pick up and handle a given message if they are placed in a competing consumer relationship.
Configuration of a consumer group mechanism is not very difficult. We just have to set a group parameter with the name of the group for the given destination.
Consumer group mechanisms is a concept taken from Apache Kafka, and implemented in Spring Cloud Stream also for RabbitMQ broker, which does not natively support it.
If you set a group name for the selected destination Spring Cloud Stream will create a single binding for all running instances of a given service. The name of the binding will be suffixed with the group name.
Durable Queues
By default, the Spring Cloud Stream consumer application creates an anonymous auto-delete queue. This can result in a message not being stored and forwarded by the producer if the producer application started before the consumer application. Even though the exchange is durable, we need a durable queue to be bound to the exchange for the message to be stored for later consumption. Hence, for guaranteed message delivery, you need a durable queue.
To pre-create durable queues and bind them to the exchange, the producer application should set the following property: spring.cloud.stream.bindings.<channelName>.producer.requiredGroups
The requiredGroups property accepts a comma-separated list of groups to which the producer must ensure message delivery. When this property is set, a durable queue is created by using the <exchange>.<requiredGroup> format.
Generic framework with support for both of these platforms
- Kafka
- RabbitMQ
KNOWLEDGE GAP - LEARN MORE, IMPLEMENT THIS
https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-stream-samples - many examples here
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-cloud-stream