Spring security - Architecture
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/architecture.html
Spring Security’s Servlet support is based on Servlet Filters. Spring Interceptors vs Servlet Filters
Key components
-
DelegatingFilterProxy- https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/architecture.html#servlet-delegatingfilterproxySpring provides a
Filterimplementation namedDelegatingFilterProxythat allows bridging between the Servlet container’s lifecycle and Spring’sApplicationContext. The Servlet container allows registeringFilterinstances by using its own standards, but it is not aware of Spring-defined Beans. You can registerDelegatingFilterProxythrough the standard Servlet container mechanisms but delegate all the work to a Spring Bean that implements Filter.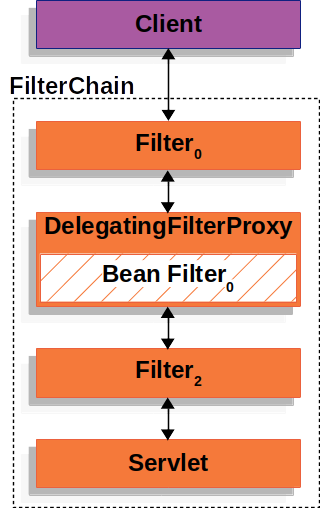
DelegatingFilterProxylooks up Bean Filter from theApplicationContextand then invokes Bean Filter. The following listing shows pseudo code ofDelegatingFilterProxy.public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) { Filter delegate = getFilterBean(someBeanName); delegate.doFilter(request, response); }-
Filter delegate = getFilterBean(someBeanName);- Lazily get Filter that was registered as a Spring Bean. -
delegate.doFilter(request, response);- Delegate work to the Spring BeanAnother benefit of
DelegatingFilterProxyis that it allows delaying looking up Filter bean instances. This is important because the container needs to register the Filter instances before the container can start up. However, Spring typically uses aContextLoaderListenerto load the Spring Beans, which is not done until after the Filter instances need to be registered.
-
-
FilterChainProxy- https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/architecture.html#servlet-filterchainproxySpring Security’s Servlet support is contained within
FilterChainProxy.FilterChainProxyis a specialFilterprovided by Spring Security that allows delegating to manyFilterinstances throughSecurityFilterChain. SinceFilterChainProxyis a Bean, it is typically wrapped in aDelegatingFilterProxy.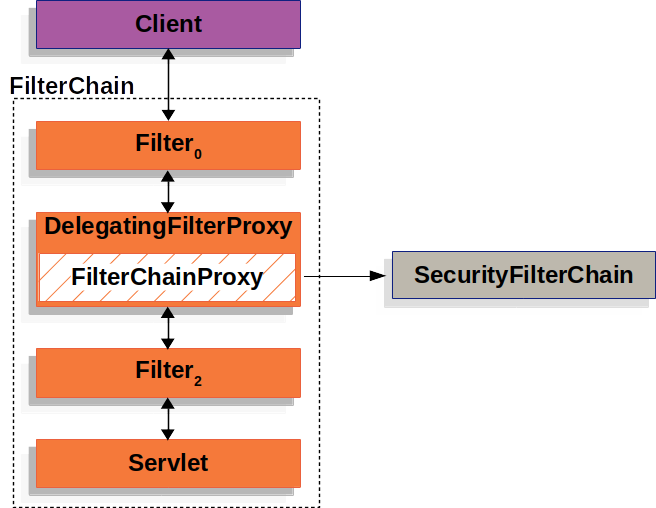
-
SecurityFilterChain- https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/architecture.html#servlet-securityfilterchainSecurityFilterChainis used byFilterChainProxyto determine which Spring SecurityFilterinstances should be invoked for the current request.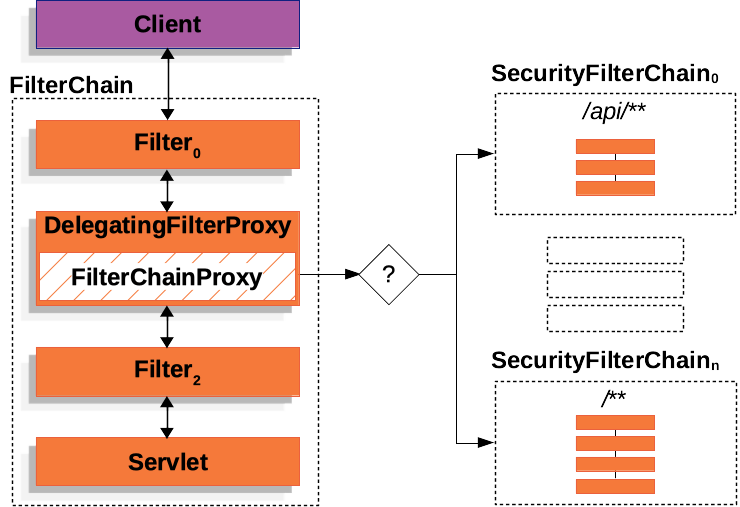
The Security Filters in SecurityFilterChain are typically Beans, but they are registered with FilterChainProxy instead of DelegatingFilterProxy. FilterChainProxy provides a number of advantages to registering directly with the Servlet container or DelegatingFilterProxy. First, it provides a starting point for all of Spring Security’s Servlet support. For that reason, if you try to troubleshoot Spring Security’s Servlet support, adding a debug point in FilterChainProxy is a great place to start.
-
Security Filters- https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/architecture.html#servlet-security-filtersThe Security Filters are inserted into the
FilterChainProxywith theSecurityFilterChainAPI. Those filters can be used for a number of different purposes, like authentication, authorization, exploit protection, and more. The filters are executed in a specific order to guarantee that they are invoked at the right time, for example, theFilterthat performs authentication should be invoked before theFilterthat performs authorization. It is typically not necessary to know the ordering of Spring Security’s Filters. However, there are times that it is beneficial to know the ordering, if you want to know them, you can check theFilterOrderRegistrationcode.- Adding a Custom Filter to the Filter Chain
@Bean SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http // ... .addFilterBefore(new TenantFilter(), AuthorizationFilter.class); return http.build(); }
- Adding a Custom Filter to the Filter Chain
-
Handling Security Exceptions - https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/architecture.html#servlet-exceptiontranslationfilter
-
Saving Requests Between Authentication - https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/architecture.html#savedrequests
-
Logging - https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/architecture.html#servlet-logging
Spring Security maintains a SecurityFilterChain internally where filters we can be added/removed from the configuration depending on the services required. Based on the services requirements, we can add or replace filters, since each filter has a specific responsibility in the filter chain.
SecurityContextIntegrationFilterResponsible to establish SecurityContext and maintaining it between HTTP requests.LogoutFilterClears the SecurityContextHolder whenever we logout.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilterThis filter is responsible to Authenticate to SecurityContext whenever we require login.ExceptionTranslationFilterResponsible for converting SpringSecurity exceptions to HTTP responses.FilterSecurityInterceptorThis filter performs security handling of HTTP resources through filter implementation. This filter also allows requests based on authorities.